You play an important role in managing your diabetes. This includes monitoring your overall health, because diabetes can cause problems with your eyes, heart, kidneys, blood vessels, nerves and limbs. The best way to reduce your risk of diabetes-related problems is to stay educated about the disease; practice skills to manage your blood sugar levels, including eating a healthy diet; and get regular checkups from your doctor.
What Are Diabetes Complications?
Complications can be short-term or long-term. Short-term problems can be life-threatening and lead to more serious conditions if left untreated. Long-term problems almost always require a lifestyle change. This could mean improving your diet, changing medication or having surgery.
Short-Term Complications
Low blood sugar
You should test your blood sugar regularly, monitor yourself for signs of low blood sugar and know your individual symptoms. Some people have few or no symptoms, which increases their risk of developing severely low levels. See the opposite side of this handout for tips on preventing low levels. But be sure to talk to your doctor about your individual target blood sugar levels.
Symptoms:
- Weakness
- Shakiness
- Hunger
- Irritability
- Headaches
- Dizziness
- Trouble concentrating
- Lightheadedness
High blood sugar
High blood sugar is a sign that your diabetes care plan may need adjusting. It’s often “silent” in its early stages, but over time it may cause a variety of symptoms. High blood sugar also increases your risk of long-term complications.
Symptoms:
- Increased thirst
- Frequent urination
- Feeling tired
- Blurred vision
- Slow-healing cuts
- Frequent infections
- Weight loss
- Vomiting
Long-Term Complications
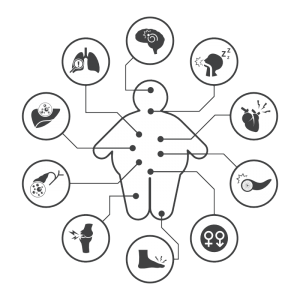
- Stroke
- Heart Attack
- Eye disease
- Kidney disease
- Amputation
What to Do When Your Blood Sugar Is Too Low or Too High
Ask your doctor when you should call to report levels that are too high or too low.
Treating low blood sugar
Always carry an emergency supply of carbohydrates and a blood sugar meter with you. These will help you be prepared to treat low blood sugar in almost any situation. For most people, blood sugar less than 70mg/dL is too low and needs to be treated immediately. Remember: When in doubt, treat your symptoms!
At the first sign of symptoms, follow these steps:
- If possible, test your blood sugar
- Eat or drink food containing 15 grams of carbohydrates, such as:
• 4 ounces of juice or regular soda
• Three to four sugar tablets
• One serving of sugar gel
• 1 cup of skim milk
• Five to six pieces of hard candy (mints), not sugar-free - Rest for 15 minutes, then retest your blood sugar
- If your blood sugar remains too low, repeat steps 2 and 3
- Eat a meal or snack within the next hour
Managing high blood sugar
To help manage high blood sugar, test it regularly. Look for things that may cause your blood sugar to rise, such as unhealthy food choices, too little medication, and stress or illness. Work with your doctor to adjust your care plan if needed, and call your doctor if your blood sugar remains above your target range for several tests and you don’t know why your blood sugar is high.
Reduce Your Risk Factors With These Lifestyle Tips
Lifestyle changes, along with taking the medications your doctor prescribes, can help reduce some risk factors for diabetes-related problems.
- Meet the blood sugar targets your doctor recommends. For many, that’s 80-130mg/dL before meals and less than 180mg/dL within one to two hours after meals.
- Keep your blood pressure levels in check.
- Exercise (be sure to talk with your doctor before beginning a program).
- Don’t smoke.
- Inspect your feet every day. Report any changes to your doctor.
- Get regular eye and dental exams, and have your cholesterol and urine tested on a schedule your doctor recommends.
- Eat high-fiber, low-fat foods, including moderate amounts of lean proteins and carbohydrates. Eat regular meals and healthy snacks. Talk with a dietitian for help developing meal plans.